Hallo Habr! Ich präsentiere Ihnen die Übersetzung des Artikels "Implementieren von RoI-Pooling in TensorFlow + Keras" von Jaime Sevilla.
Ich nehme derzeit an einem maschinellen Lernkurs teil. Im Trainingsblock "Computer Vision" musste das RoI-Pooling von Schichten untersucht werden. Der folgende Artikel schien mir interessant zu sein, und deshalb habe ich beschlossen, die Übersetzung mit der Community zu teilen.
In diesem Beitrag werden das Grundkonzept und die allgemeine Verwendung des RoI-Poolings ( Region of Interest ) erläutert und eine Implementierung mithilfe von TensorFlow-Keras-Ebenen bereitgestellt.
Die Zielgruppe dieses Beitrags sind Personen, die mit der Grundtheorie der (Faltungs-) Neuronalen Netze (CNNs) vertraut sind und einfache Modelle mit Keras erstellen und ausführen können .
Wenn Sie nur für Code hier sind, überprüfen Sie hier und vergessen Sie nicht, den Artikel zu mögen und zu teilen!
Grundlegendes zum RoI-Pooling
RoI Pooling wurde von Ross Girshik in einem Artikel über Fast R-CNN als Teil seiner Objekterkennungspipeline vorgeschlagen.
In einem allgemeinen Anwendungsfall für das RoI-Pooling haben wir ein bildähnliches Objekt und mehrere interessierende Regionen ( RoIs ), die durch Begrenzungsrahmen angegeben werden. Wir möchten Einbettungen (Einbettungen - Zuordnung einer beliebigen Entität (eines Bildstücks) zu einem bestimmten Vektor) aus jedem RoI erstellen.
In einem R-CNN-Setup haben wir beispielsweise ein Bild und eine Engine zum Hervorheben von Kandidatenregionen, die Begrenzungsrahmen für potenziell interessante Teile des Bildes erstellen. Jetzt möchten wir für jedes vorgeschlagene Bildstück eine Einbettung erstellen.
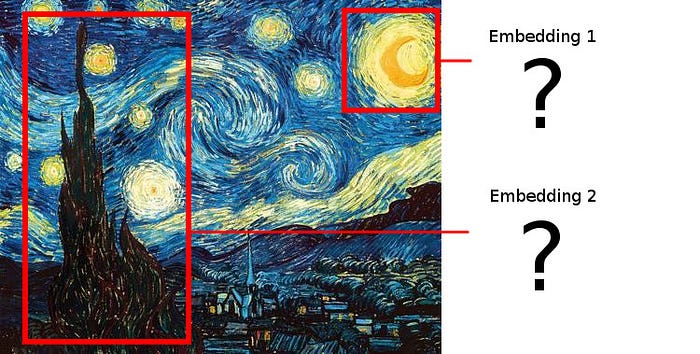
Das einfache Zuschneiden jedes vorgeschlagenen Bereichs funktioniert nicht, da wir die resultierenden Einbettungen übereinander legen möchten und die vorgeschlagenen Bereiche nicht unbedingt dieselbe Form haben müssen!
, . ?
- (pooling).
max pooling, ( ) , , .

maxpool
, – : .
. RoI ?

ROI Pooling , pooling.
, ROI Pooling.
RoI Pooling.
RoI Pooling — . , RoI, . , .
-, ( RoI Pooling ), ( ), (end-to-end) (single-pass) .
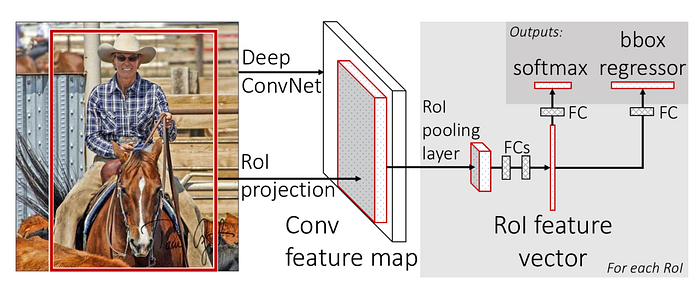
Fast R-CNN, RoI Pooling,
, R-CNN , (RoI). RoI Pooling CNN . .
-, -, RoI Pooling (visual attention).
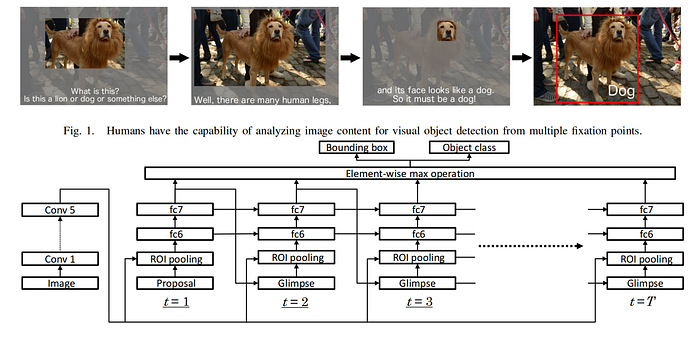
Attentional Network , ROI Pooling, Hara ..
Attentional Network , Hara attention, ROI ROI Pooling. (t = 1), ROI Pooling (Fully Connected). Glimpse () (t = 2) , ROI Pooling. .
.
, , ROI.
:
- (batch) . , . (batch_size, img_width, img_height, n_channels), batch_size- , img_width — , img_height — , n_channels — .
- (batch) ROI. , - . 4 , (batch_size, n_rois, 4), batch_size — ROI, n_rois — ROI.
:
- , ROI. (batch_size, n_rois, pooled_width, pooled_height, n_channels). batch_size- , n_rois — ROI, pooled_width — , pooled_height— , n_channels — .
Keras
Keras Layer.
tf.keras init, build call . , build , , . compute_output_shape.
, .
def __init__(self, pooled_height, pooled_width, **kwargs):
self.pooled_height = pooled_height
self.pooled_width = pooled_width
super(ROIPoolingLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs). , . .
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
""" Returns the shape of the ROI Layer output
"""
feature_map_shape, rois_shape = input_shape
assert feature_map_shape[0] == rois_shape[0]
batch_size = feature_map_shape[0]
n_rois = rois_shape[1]
n_channels = feature_map_shape[3]
return (batch_size, n_rois, self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width, n_channels)compute_output_shape — , , .
(call). — , . , ROI Pooling, .
, , ROI .
.
@staticmethod
def _pool_roi(feature_map, roi, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI Pooling to a single image and a single ROI
"""# Compute the region of interest
feature_map_height = int(feature_map.shape[0])
feature_map_width = int(feature_map.shape[1])
h_start = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[0], 'int32')
w_start = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[1], 'int32')
h_end = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[2], 'int32')
w_end = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[3], 'int32')
region = feature_map[h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end, :]
..., .
, ROI , 0 1. , ROI 4- , (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max ).
ROI , , , : , , ROI Pooling, , , ROI.
, TensorFlow.
...
# Divide the region into non overlapping areas
region_height = h_end - h_start
region_width = w_end - w_start
h_step = tf.cast(region_height / pooled_height, 'int32')
w_step = tf.cast(region_width / pooled_width , 'int32')
areas = [[(
i*h_step,
j*w_step,
(i+1)*h_step if i+1 < pooled_height else region_height,
(j+1)*w_step if j+1 < pooled_width else region_width
)
for j in range(pooled_width)]
for i in range(pooled_height)]
...ROI, .
2D , , , .
, , , , ROI (region_height // pooled_height, region_width // pooled_width), ROI, .
2D , .
...
# Take the maximum of each area and stack the result
def pool_area(x):
return tf.math.reduce_max(region[x[0]:x[2],x[1]:x[3],:], axis=[0,1])
pooled_features = tf.stack([[pool_area(x) for x in row] for row in areas])
return pooled_features . pool_area, , , , , .
pool_area , , list comprehension .
(pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels), RoI .
— RoI . tf.map_fn (n_rois, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels).
@staticmethod
def _pool_rois(feature_map, rois, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI pooling for a single image and varios ROIs
"""
def curried_pool_roi(roi):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_roi(feature_map, roi,
pooled_height, pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_roi, rois, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas, . tf.map_fn (, x), , .
def call(self, x):
""" Maps the input tensor of the ROI layer to its output
"""
def curried_pool_rois(x):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_rois(x[0], x[1],
self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_rois, x, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas, dtype tf.map_fn , . , , , Tensorflow.
:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Layer
class ROIPoolingLayer(Layer):
""" Implements Region Of Interest Max Pooling
for channel-first images and relative bounding box coordinates
# Constructor parameters
pooled_height, pooled_width (int) --
specify height and width of layer outputs
Shape of inputs
[(batch_size, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels),
(batch_size, num_rois, 4)]
Shape of output
(batch_size, num_rois, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels)
"""
def __init__(self, pooled_height, pooled_width, **kwargs):
self.pooled_height = pooled_height
self.pooled_width = pooled_width
super(ROIPoolingLayer, self).__init__(**kwargs)
def compute_output_shape(self, input_shape):
""" Returns the shape of the ROI Layer output
"""
feature_map_shape, rois_shape = input_shape
assert feature_map_shape[0] == rois_shape[0]
batch_size = feature_map_shape[0]
n_rois = rois_shape[1]
n_channels = feature_map_shape[3]
return (batch_size, n_rois, self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width, n_channels)
def call(self, x):
""" Maps the input tensor of the ROI layer to its output
# Parameters
x[0] -- Convolutional feature map tensor,
shape (batch_size, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels)
x[1] -- Tensor of region of interests from candidate bounding boxes,
shape (batch_size, num_rois, 4)
Each region of interest is defined by four relative
coordinates (x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max) between 0 and 1
# Output
pooled_areas -- Tensor with the pooled region of interest, shape
(batch_size, num_rois, pooled_height, pooled_width, n_channels)
"""
def curried_pool_rois(x):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_rois(x[0], x[1],
self.pooled_height,
self.pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_rois, x, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas
@staticmethod
def _pool_rois(feature_map, rois, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI pooling for a single image and varios ROIs
"""
def curried_pool_roi(roi):
return ROIPoolingLayer._pool_roi(feature_map, roi,
pooled_height, pooled_width)
pooled_areas = tf.map_fn(curried_pool_roi, rois, dtype=tf.float32)
return pooled_areas
@staticmethod
def _pool_roi(feature_map, roi, pooled_height, pooled_width):
""" Applies ROI pooling to a single image and a single region of interest
"""
# Compute the region of interest
feature_map_height = int(feature_map.shape[0])
feature_map_width = int(feature_map.shape[1])
h_start = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[0], 'int32')
w_start = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[1], 'int32')
h_end = tf.cast(feature_map_height * roi[2], 'int32')
w_end = tf.cast(feature_map_width * roi[3], 'int32')
region = feature_map[h_start:h_end, w_start:w_end, :]
# Divide the region into non overlapping areas
region_height = h_end - h_start
region_width = w_end - w_start
h_step = tf.cast( region_height / pooled_height, 'int32')
w_step = tf.cast( region_width / pooled_width , 'int32')
areas = [[(
i*h_step,
j*w_step,
(i+1)*h_step if i+1 < pooled_height else region_height,
(j+1)*w_step if j+1 < pooled_width else region_width
)
for j in range(pooled_width)]
for i in range(pooled_height)]
# take the maximum of each area and stack the result
def pool_area(x):
return tf.math.reduce_max(region[x[0]:x[2], x[1]:x[3], :], axis=[0,1])
pooled_features = tf.stack([[pool_area(x) for x in row] for row in areas])
return pooled_features! , 1- 100x200, 2 RoI, 7x3. , 4 . — 1, 50 (-1, -3).
import numpy as np# Define parameters
batch_size = 1
img_height = 200
img_width = 100
n_channels = 1
n_rois = 2
pooled_height = 3
pooled_width = 7# Create feature map input
feature_maps_shape = (batch_size, img_height, img_width, n_channels)
feature_maps_tf = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=feature_maps_shape)
feature_maps_np = np.ones(feature_maps_tf.shape, dtype='float32')
feature_maps_np[0, img_height-1, img_width-3, 0] = 50
print(f"feature_maps_np.shape = {feature_maps_np.shape}")# Create batch size
roiss_tf = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(batch_size, n_rois, 4))
roiss_np = np.asarray([[[0.5,0.2,0.7,0.4], [0.0,0.0,1.0,1.0]]], dtype='float32')
print(f"roiss_np.shape = {roiss_np.shape}")# Create layer
roi_layer = ROIPoolingLayer(pooled_height, pooled_width)
pooled_features = roi_layer([feature_maps_tf, roiss_tf])
print(f"output shape of layer call = {pooled_features.shape}")# Run tensorflow session
with tf.Session() as session:
result = session.run(pooled_features,
feed_dict={feature_maps_tf:feature_maps_np,
roiss_tf:roiss_np})
print(f"result.shape = {result.shape}")
print(f"first roi embedding=\n{result[0,0,:,:,0]}")
print(f"second roi embedding=\n{result[0,1,:,:,0]}"), TensorFlow, .
:
feature_maps_np.shape = (1, 200, 100, 1)
roiss_np.shape = (1, 2, 4)
output shape of layer call = (1, 2, 3, 7, 1)
result.shape = (1, 2, 3, 7, 1)
first roi embedding=
[[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]
second roi embedding=
[[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[ 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 1. 50.]], . — 1, , 50.
, !
, !
, ROI Pooling (attention). , , Keras , ROI Pooling .
, , , !
Ari Brill, Tjark Miener Bryan Kim .
- Ross Girshick. Fast R-CNN. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. 2015.
- Kota Hara, Ming-Yu Liu, Oncel Tuzel, Amir-massoud Farahmand. Attentional Network for Visual Object Detection. 2017.