
Heute werde ich Sie durch die Echtzeit-Fehlerverfolgung in einer React-App führen. Eine Frontend-Anwendung wird normalerweise nicht zur Fehlerverfolgung verwendet. Einige Unternehmen verschieben häufig die Verfolgung von Fehlern, indem sie nach Dokumentation, Tests und mehr darauf zurückgreifen. Wenn Sie Ihr Produkt jedoch zum Besseren verändern können, tun Sie es einfach!
1. Warum brauchst du Sentry?
Ich gehe davon aus, dass Sie daran interessiert sind, Fehler während der Produktion zu verfolgen
Glaubst du, das ist nicht genug?
Ok, lass uns die Details sehen.
Hauptgründe für die Verwendung von Sentry für Entwickler:
- Beseitigt das Risiko der Bereitstellung von fehlerhaftem Code
- QS-Unterstützung beim Codetest
- Erhalten Sie schnelle Benachrichtigungen über Probleme
- Die Fähigkeit, Fehler schnell zu beheben
- Bequeme Anzeige von Fehlern im Admin-Bereich
- Sortierfehler nach Benutzer- / Browsersegment
Die Hauptgründe für den CEO / Lead des Projekts
- Geld sparen (Sentry kann auf Ihren Servern installiert werden)
- Benutzerfeedback erhalten
- Echtzeit-Verständnis dafür, was mit Ihrem Projekt nicht stimmt
- Verstehen der Anzahl der Probleme, die Menschen mit Ihrer Anwendung haben
- Helfen Sie dabei, Orte zu finden, an denen Ihre Entwickler einen Fehler gemacht haben
, . , Sentry.
.
?

Sentry?
Sentry – , , . , . Sentry JavaScript, Node, Python, PHP, Ruby, Java .

2.
- Sentry . , . ( Sentry )
- . ( React. « »)
. , Sentry , :
import * as Sentry from '@sentry/browser';
// Sentry.init({
// dsn: "<https://63bbb258ca4346139ee533576e17ac46@sentry.io/1432138>"
// });
// should have been called before using it here
// ideally before even rendering your react app
class ExampleBoundary extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { error: null };
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
this.setState({ error });
Sentry.withScope(scope => {
Object.keys(errorInfo).forEach(key => {
scope.setExtra(key, errorInfo[key]);
});
Sentry.captureException(error);
});
}
render() {
if (this.state.error) {
//render fallback UI
return (
<a onClick={() => Sentry.showReportDialog()}>Report feedback</a>
);
} else {
//when there's not an error, render children untouched
return this.props.children;
}
}
}Sentry , , . . , . , !
3. React Sentry
npm .
npm i @sentry/browserSentry :
Sentry.init({
// dsn: #dsnUrl,
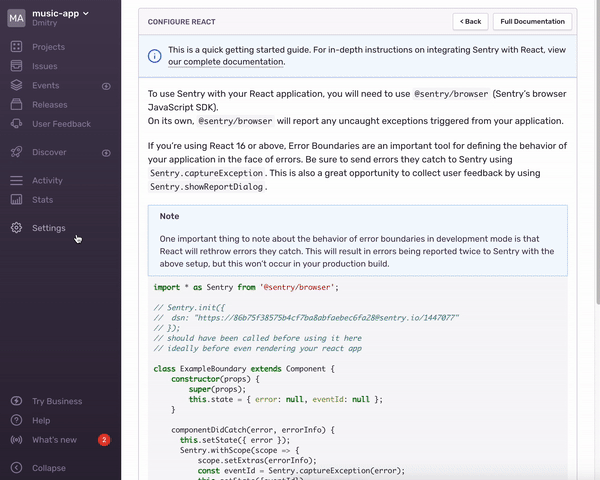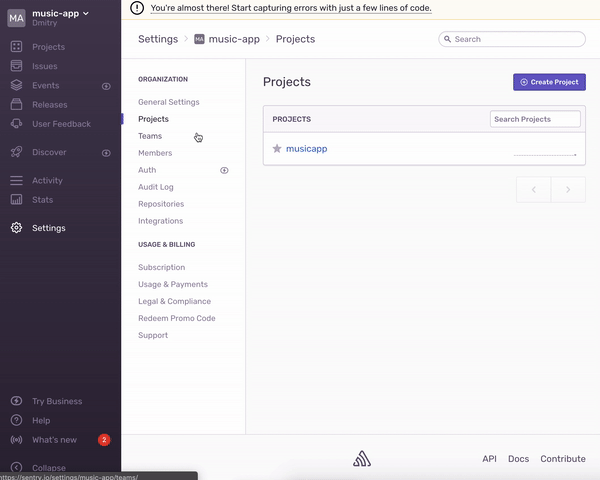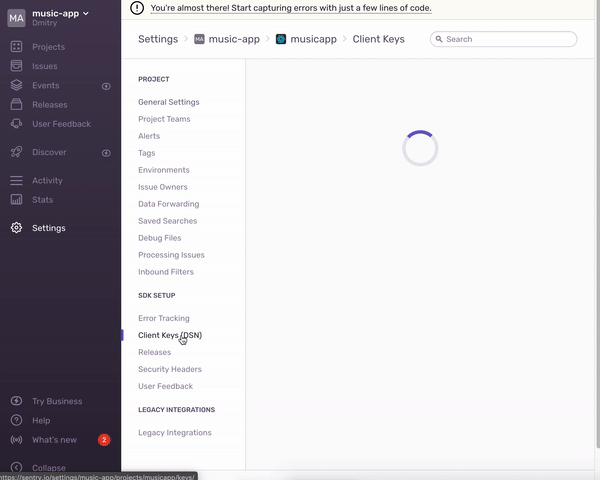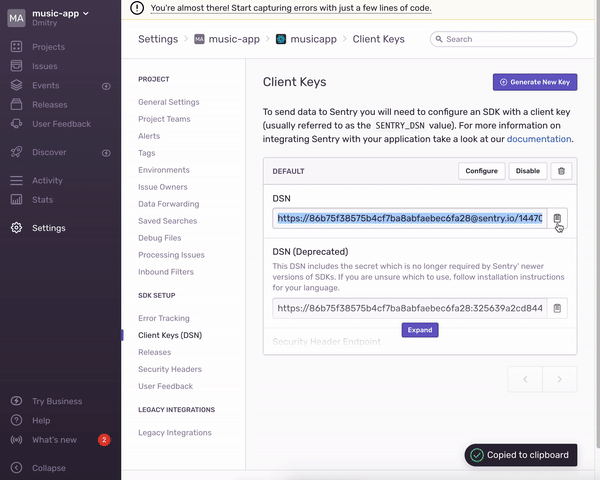
});DSN Projects -> Settings -> Client Keys. .
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
Sentry.withScope(scope => {
Object.keys(errorInfo).forEach(key => {
scope.setExtra(key, errorInfo[key]);
});
Sentry.captureException(error);
});
}4.
, console.log user.email. : Uncaught TypeError ( email) - . Javascript.
<button type="button" onClick={() => console.log(user.email)}>
Test Error button
</button>:
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { Input, List, Skeleton, Avatar } from "antd";
import * as Sentry from "@sentry/browser";
import getList from "../store/actions/getList";
const Search = Input.Search;
const mapState = state => ({
list: state.root.list,
loading: state.root.loading
});
const mapDispatch = {
getList
};
class Container extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
Sentry.init({
dsn: "https://fc0edcf6927a4397855797a033f04085@sentry.io/1417586",
});
}
componentDidCatch(error, errorInfo) {
Sentry.withScope(scope => {
Object.keys(errorInfo).forEach(key => {
scope.setExtra(key, errorInfo[key]);
});
Sentry.captureException(error);
});
}
render() {
const { list, loading, getList } = this.props;
const user = undefined;
return (
<div className="App">
<button
type="button"
onClick={() => console.log(user.email)}
>
test error1
</button>
<div onClick={() => Sentry.showReportDialog()}>Report feedback1</div>
<h1>Music Finder</h1>
<br />
<Search onSearch={value => getList(value)} enterButton />
{loading && <Skeleton avatar title={false} loading={true} active />}
{!loading && (
<List
itemLayout="horizontal"
dataSource={list}
locale={{ emptyText: <div /> }}
renderItem={item => (
<List.Item>
<List.Item.Meta
avatar={<Avatar src={item.artist.picture} />}
title={item.title}
description={item.artist.name}
/>
</List.Item>
)}
/>
)}
</div>
);
}
}
export default connect(
mapState,
mapDispatch
)(Container);.
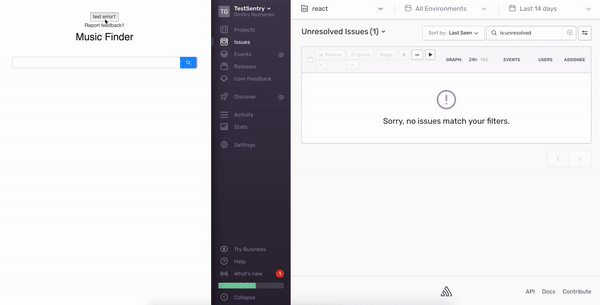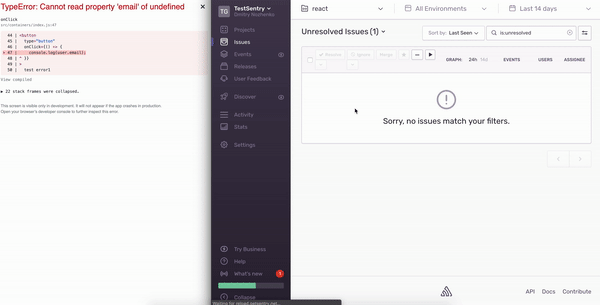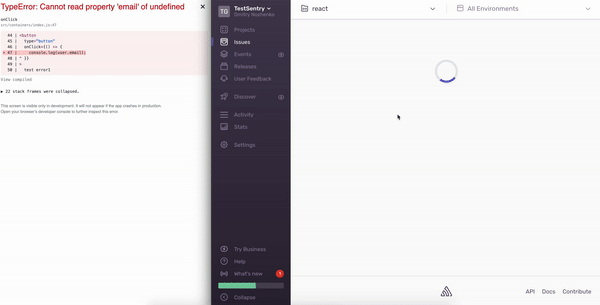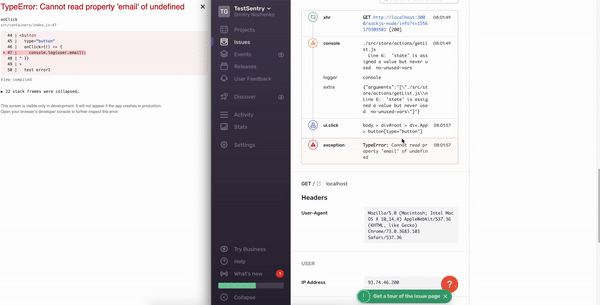

Whoo-hoo!

, .
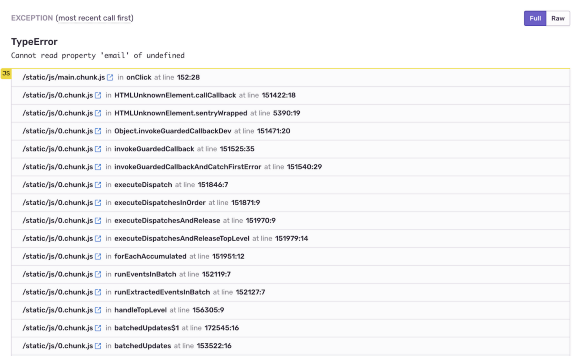
. , , , . ReactJS, .
, , .
. , Dmitry Nozhenko source map. , Dmitry Nozhenko, .
5. Sentry API
. javascript . , XHR?
Sentry . api.
Sentry.captureException(err), , , , . .
superagent
.get(`https://deezerdevs-deezer.p.rapidapi.com/search?q=${query}`)
.set("X-RapidAPI-Key", #id_key)
.end((err, response) => {
if (err) {
Sentry.configureScope(
scope => scope
.setUser({"email": "john.doe@example.com"})
.setLevel("Error")
);
return Sentry.captureException(err);
}
if (response) {
return dispatch(setList(response.body.data));
}
});API catch.
import * as Sentry from "@sentry/browser";
export const apiCatch = (error, getState) => {
const store = getState();
const storeStringify = JSON.stringify(store);
const { root: { user: { email } } } = store;
Sentry.configureScope(
scope => scope
.setLevel("Error")
.setUser({ email })
.setExtra("store", storeStringify)
);
// Sentry.showReportDialog(); - If you want get users feedback on error
return Sentry.captureException(error);
};api.
export default query => (dispatch, getState) => {
superagent
.get(`https://deezerdevs-deezer.p.rapidapi.com/search?q=${query}`)
.set("X-RapidAPI-Key", #id_key)
.end((error, response) => {
if (error) {
return apiCatch(error, getState)
}
if (response) {
return dispatch(setList(response.body.data));
}
});
};:
- setLevel sentry. — ‘fatal’, ‘error’, ‘warning’, ‘log’, ‘info, ‘debug’, ‘critical’).
- setUser (id, , . .).
- setExtra , , , .
Wenn Sie Benutzerfeedback zu einem Fehler erhalten möchten, sollten Sie die Funktion showReportDialog verwenden.
Sentry.showReportDialog();Ausgabe:
Heute haben wir eine Möglichkeit beschrieben, Sentry in eine React-App zu integrieren.
→ Telegramm-Chat über Sentry